Circular 07/2025, effective from 5 May 2025, introduces the most comprehensive update to Vietnam’s joint training regulations in more than a decade. It establishes clear parameters for international cooperation, delivery models, teaching responsibilities and compliance. For Vietnamese institutions, foreign partners and students, the Circular provides long-awaited clarity and defines a more predictable environment for internationalised higher education.
This article outlines the key provisions of Circular 07/2025 and examines what they mean for strategic planning, compliance and future opportunities.
1. Scope and Definitions
Circular 07/2025 applies to all joint training programmes delivered by Vietnamese universities in partnership with foreign higher education institutions. It covers bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral levels and defines three approved delivery models.
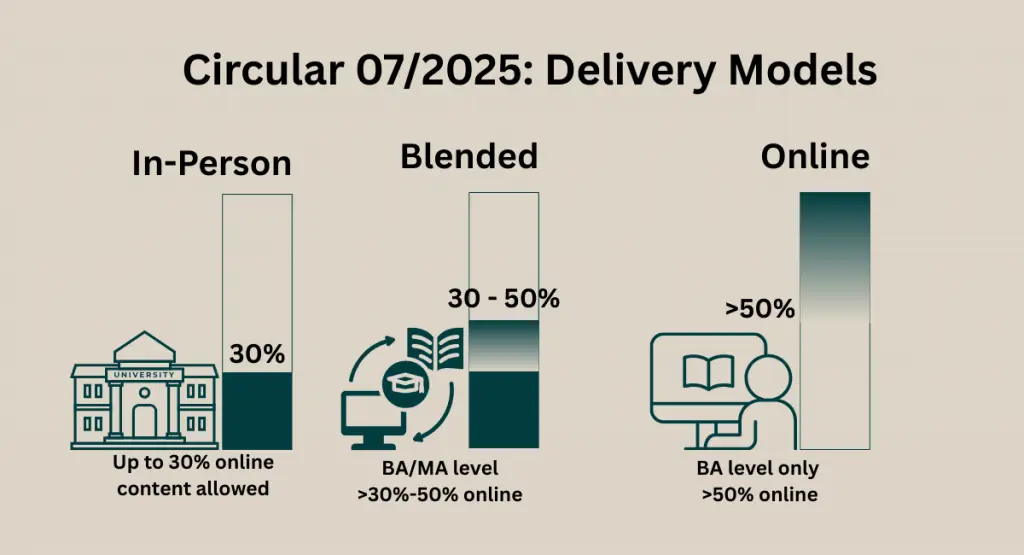
2. Delivery Models
The Circular provides precise thresholds for program structure and online delivery:
In-Person Programs
May include up to 30% online components.
Blended Programs
Applicable to bachelor’s and master’s levels.
Must include more than 30% and up to 50% online delivery.
Fully Online Programs
Permitted only at the bachelor’s level.
Must include more than 50% online delivery.
This clarity marks a shift from previously ambiguous provisions and provides institutions with a structured basis for programme design and approval.
3. Teaching Responsibilities
Foreign partner institutions must deliver at least 25% of the programme content and carry full responsibility for this portion. This ensures a demonstrable international academic contribution and supports alignment with external standards.
4. Admissions and Student Requirements
Enrolment in joint programmes counts toward the Vietnamese institution’s annual admission quota.
Students must meet Vietnam’s six-level foreign language framework, verified through:
Approved language certificates
Degrees in foreign-language majors assessed against the framework
Full-time degrees completed abroad
Institutions may offer up to 12 months of preparatory language training before programme commencement.
5. Academic and Compliance Requirements
Compulsory Subjects
Vietnamese students must complete all nationally mandated subjects, regardless of delivery model.
Oversight and Reporting
Institutions must:
Establish internal regulations
Supervise programme delivery
Report to the Higher Education Management Information System (HEMIS) as required
Transition Arrangements
Programmes approved before 5 May 2025 may continue until completion. New programmes or extensions must comply fully with Circular 07/2025.
6. Why the Circular Matters
Joint programmes have expanded rapidly in Vietnam, often operating in regulatory uncertainty. Circular 07 provides consistency and transparency in three essential areas:
Institutional Strategy
It offers a clear framework for designing programmes that meet national expectations and international standards.
Market Confidence
Predictable rules reduce administrative risk for both Vietnamese universities and foreign institutions.
Student Protection
Learners gain clearer pathways, improved quality assurance and more flexible study options.

7. Opportunities for Key Stakeholders
For Vietnamese Universities
Expand reach through blended and online provision
Diversify revenue beyond on-campus tuition
Demonstrate compliance through transparent reporting and quality processes
For Foreign Partners
Enter the Vietnamese market with clearer approval pathways
Deliver hybrid programmes aligned with student demand
Strengthen institutional reputation by meeting the 25% teaching requirement
For Students
Access flexible learning models
Benefit from combined local and international academic expertise
Reduce financial barriers compared to full overseas study
8. Implementation Challenges
Successful adoption will require more than regulatory compliance. Key challenges include:
Ensuring quality and consistency in online and blended delivery
Building digital capacity and training staff
Supporting students in regions with limited connectivity
Strengthening administrative capabilities in data management and reporting
9. A Readiness Checklist for Leaders
To prepare for implementation, institutions should:
Confirm alignment with the Circular’s delivery model thresholds
Assess digital infrastructure and student support systems
Plan faculty and partner contributions to meet the 25% requirement
Monitor admissions against institutional quotas
Provide clear guidance on language requirements and preparatory pathways
Conclusion
Circular 07/2025 signals Vietnam’s commitment to aligning internationalised higher education with clear regulatory standards and strong oversight. While it raises expectations for institutional capability, it also creates new opportunities for partnerships, innovation and expanded access. Institutions that build high-quality, compliant and student-centred joint programmes will gain a competitive advantage and contribute meaningfully to Vietnam’s position as an emerging education hub in the ASEAN region.
